Mastering the Art of Cutting Large Stone Blocks: A Guide to Essential Equipment
The craft of cutting large stone blocks has been refined over centuries, evolving from the laborious hand chiseling of ancient stonemasons to the sophisticated machinery used today. The ability to precisely cut stone is crucial in various industries, from construction and landscaping to sculpture and masonry. This article explores the various kinds of equipment designed for stone block cutting, offering insights into their functions, advantages, and applications.


CNC Block Wire Saws:
One of the most prevalent tools for cutting large stone blocks is the wire saw. These saws use a metal wire or cable coated with diamond-tipped beads, which can slice through stone with precision. Wire saws are particularly useful for their ability to cut massive blocks and for intricate shapes that other saws may struggle with. They are often used in quarrying to extract natural stone slabs and in construction for cutting sections of concrete.
Wire saws are sophisticated stone-cutting machines that offer precision and efficiency in slicing through large stone blocks. Below is an in-depth look at the components, operation, and benefits of using wire saws in the stone cutting industry.
Components of Wire Saws:
Wire:
The core component of a wire saw is a long, flexible wire or cable. This wire is impregnated with diamond or silicon carbide beads at regular intervals. The hardness of these materials allows the wire to cut through stone with ease.
Driving Wheels:
These are the pulleys or wheels that move the wire through the stone. They are powered by an electric motor or a hydraulic system, providing the necessary force to propel the wire.
Tensioning System:
To ensure efficient cutting, the wire must be kept under constant tension. The tensioning system adjusts the tension on the wire to prevent it from sagging or snapping during the cutting process.
Cooling System:
Cutting stone generates a significant amount of heat due to friction. A cooling system, often using water, is essential to prevent overheating, which can damage both the wire and the stone.
Guidance System:
This system guides the wire saw along the desired cutting path. It can be manually operated or computer-controlled for precision cuts.
Operation of Wire Saws:
1. Setup:
The wire is looped around the driving wheels and the stone block that needs to be cut. The tensioning system is adjusted to ensure the wire is taut.
2. Cutting Process:
The driving wheels are activated, and the wire begins to move at high speed. The operator guides the wire saw along the predetermined path, or if CNC-controlled, the machine follows a programmed route.
3. Cooling:
As the wire saw operates, water is continuously sprayed onto the cutting area to cool the wire and stone, reducing dust and extending the life of the wire.
4. Monitoring:
Throughout the cutting process, the tension of the wire and the overall operation are monitored to ensure safety and precision.

Benefits of Using Wire Saws:
Versatility:
Wire saws can cut through almost any type of stone, regardless of its hardness. They can also handle irregular shapes and sizes with ease.
Precision:
The ability to make precise cuts with minimal kerf loss (the amount of material lost during cutting) is a significant advantage of wire saws.
Efficiency:
Wire saws can cut large blocks much more quickly than traditional methods, saving time and labor costs.
Minimal Damage:
The flexibility of the wire allows for cutting without putting excessive stress on the stone, reducing the risk of cracks or breaks outside of the intended cutting line.
Safety:
Wire saws produce less dust and vibration compared to other cutting methods, which is better for operator safety and comfort.
Wire saws are integral to modern stone quarrying and processing, enabling intricate designs and efficient material handling that were once impossible with older cutting technologies. Their use spans across various industries, from monumental stone carving to construction and demolition. With advancements in diamond technology and computer controls, wire saws continue to push the boundaries of what can be achieved in stone cutting.


Lifetime of diamond wire in CNC block wire saw machines
The lifetime of the wire in wire saw machines is influenced by several factors, many of which are related to the operating conditions and the characteristics of the material being cut. Here are some key factors that can affect the longevity of wire saw wires:
1. Abrasiveness of the Material:
The more abrasive the material being cut, the faster the wire will wear out. For instance, cutting granite, which is highly abrasive, will typically result in shorter wire life compared to cutting marble.
2. Wire Speed:
The speed at which the wire moves can impact its lifespan. Too fast, and the increased friction can cause premature wear; too slow, and it can result in inefficient cutting and potential wire fatigue.
3. Tension on the Wire:
Proper tension is crucial for wire life. If the wire is too tense, it can snap or wear out quickly due to overstress. Insufficient tension can lead to slippage or bending of the wire, causing uneven wear or breakage.
4. Cutting Parameters:
The depth of cut and feed rate need to be optimized for the type of stone being cut. Aggressive cutting parameters can lead to increased wear or potential breakage of the wire.
5. Cooling and Lubrication:
Adequate cooling and lubrication reduce frictional heat, which can degrade the wire. Insufficient cooling can lead to overheating and accelerated wear.
6. Quality of the Wire:
The manufacturing quality of the wire itself, including the quality of the diamond beads and their bond to the wire, significantly affects lifespan. Higher quality wires with well-bonded diamonds will last longer.
7. Maintenance:
Regular maintenance of the wire saw machine, including proper alignment and tensioning, ensures that the wire is not subjected to uneven forces that could shorten its life.
8. Operator Skill:
Experienced operators who can adjust cutting parameters in response to the feedback from the cutting process can extend wire life by preventing overloading and optimizing cutting conditions.
9. Pulley and Drive Wheel Condition:
Worn or misaligned pulleys can cause additional friction and wear on the wire, reducing its lifespan.
10. Environmental Factors:
The presence of dust, dirt, or other contaminants can affect the wear rate of the wire. Harsh operating environments can also contribute to quicker degradation.
11. Frequency of Use:
The more frequently a wire saw is used, the faster the wire will wear out simply due to cumulative cutting time.
12. Type of Cuts:
Straight cuts tend to be less wearing on wires than intricate patterns or shapes that require more complex wire movements and potentially more contact with abrasive surfaces.
By understanding and managing these factors, operators can optimize the performance and extend the lifespan of wire saw wires, leading to more efficient and cost-effective stone cutting operations.

Stone Block Cutters:
Block cutters are heavy-duty machines designed specifically for cutting stone blocks into desired sizes. They can be either stationary or movable and usually feature a large blade that can be raised and lowered onto the stone. The blades are often embedded with diamonds to enhance their cutting capabilities. Block cutters are ideal for producing uniform slabs and are commonly used in the production of countertops, tiles, and architectural elements.
Block cutters, also known as stone block cutters or stone splitters, are robust machines designed to segment large stone blocks into smaller, more manageable pieces or specific shapes and sizes suitable for various applications. These machines are integral to the stone industry, particularly in areas like countertop manufacturing, tile production, and architectural stonework. Here’s a detailed look at block cutters:

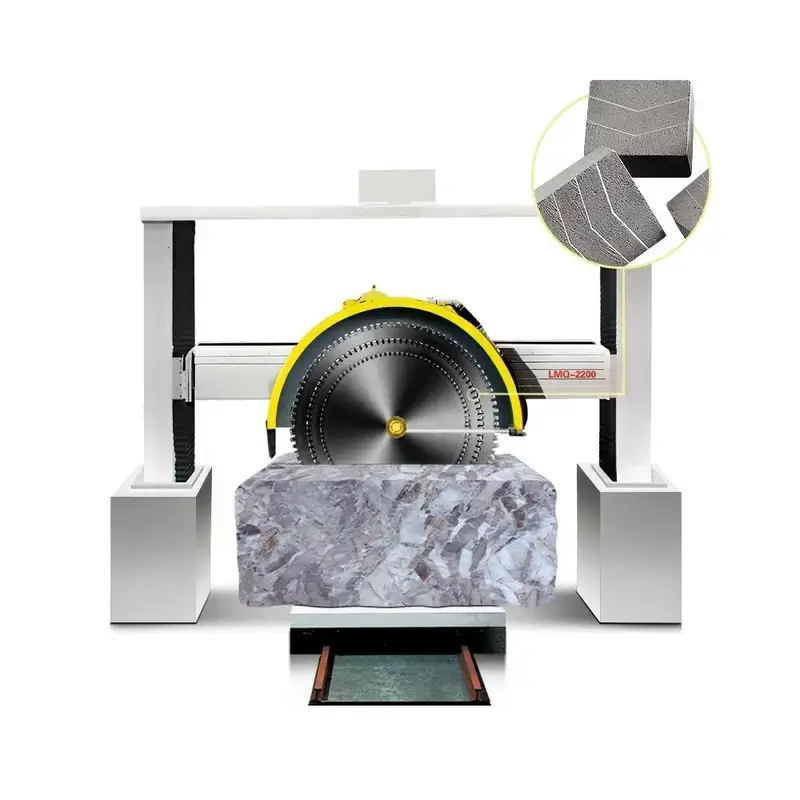
Components of Stone Block Cutters:
Frame:
The frame is the sturdy structure that supports all other components of the block cutter. It is designed to withstand the heavy loads and vibrations of cutting large stone blocks.
Cutting Blade:
The heart of the block cutter is its blade. Typically, these blades are large, circular saws with diamond-tipped teeth to cut through stone efficiently. Some block cutters might use a series of smaller blades or wires, depending on the intended application.
Motor:
The motor powers the cutting blade and is usually an electric motor strong enough to handle the resistance of cutting through stone. The horsepower required can vary depending on the size of the blade and the type of stone being cut.
Control Panel:
This is the interface where the operator manages the cutting process. It may include controls for blade speed, cutting depth, feed rate, and sometimes even programmable settings for repeated cuts.
Carriage:
A carriage or bed is where the stone block rests during the cutting process. In some models, this carriage can be moved up and down or back and forth to feed the stone into the blade.
Cooling System:
Like wire saws, block cutters also generate a lot of heat due to friction. Therefore, they are equipped with a cooling system that typically uses water to cool the blade and wash away stone dust.

Operation of Block Cutters:
1. Positioning:
The stone block is placed on the machine’s carriage. It must be securely fixed to prevent any movement during the cutting process.
2. Setting:
The operator sets the desired dimensions for cutting, adjusting the blade’s depth and position according to the size of the block and the required thickness of the slabs.
3. Cutting:
Once everything is in place, the motor is switched on, and the blade begins to spin. The carriage feeds the stone into the blade at a controlled pace to ensure a clean cut.
4. Cooling:
Water is sprayed onto the blade and stone to prevent overheating. This also helps to reduce dust emission.
5. Repetition:
For multiple cuts, the process is repeated with adjustments made to accommodate the desired sizes of subsequent slabs or blocks.

Benefits of Using Block Cutters:
Efficiency:
Block cutters can quickly process large stone blocks into slabs or smaller blocks, significantly increasing productivity.
Precision:
They are capable of making straight, clean cuts with uniform thickness, which is essential for products like tiles and countertops.
Versatility:
While primarily used for straight cuts, some advanced block cutters can be set up for angled cuts or to produce curved edges.
Durability:
Block cutters are built to last. They are designed to handle the stresses of cutting hard materials day in and day out.
Block cutters are indispensable in settings where large volumes of stone need to be consistently cut to specific dimensions. They represent a perfect blend of traditional stone cutting techniques with modern technology, providing reliability and precision in today’s demanding stone industry.
Lifetime of Blades in Block Cutter Machines
The lifetime of blades in block cutter machines is influenced by a variety of factors, which can be broadly categorized into material characteristics, operational parameters, machine condition, and maintenance practices. Here are some key factors that can affect the longevity of block cutter blades:
1. Material Hardness and Abrasiveness:
Harder and more abrasive materials will cause more wear on the blades. For example, cutting granite will typically wear down a blade faster than cutting limestone or marble.
2. Blade Quality:
The quality of the diamond segments on the blade, the quality of the steel core, and how the diamonds are bonded to the core all play a significant role in determining blade life.
3. Cutting Speed:
Operating the blade at an optimal speed that matches the material being cut is crucial. Too fast may cause excessive wear or even blade damage, while too slow can result in inefficient cutting and reduced blade life.
4. Feed Rate:
The rate at which the stone is fed into the blade affects the wear on the blade. A feed rate that’s too aggressive can overburden the blade and lead to premature wear or breakage.
5. Cooling and Lubrication:
Adequate water flow is essential for cooling and lubricating the blade during cutting. Insufficient cooling can lead to overheating, which can damage both the diamond segments and the steel core.
6. Cutting Technique:
The method of cutting, such as step cutting (making incremental depth cuts) versus slicing (cutting through the full depth in one pass), can impact blade life. Step cutting generally extends blade life.
7. Blade Tension:
Blades need to be properly tensioned in the machine. Incorrect tension can lead to blade flutter or distortion, causing uneven wear or even breakage.
8. Machine Condition:
A well-maintained block cutter with proper alignment and no vibration will extend blade life. Worn bearings or a misaligned spindle can cause irregular wear and tear on the blade.
9. Operator Skill:
Skilled operators who understand the cutting process and can make adjustments in response to feedback from the machine will generally achieve longer blade life.
10. Segment Weld Integrity:
The method used to attach the diamond segments to the steel core (laser welding, sintering, etc.) affects durability. Poorly attached segments can come off prematurely.
11. Environmental Factors:
The operating environment, including temperature and cleanliness of the work area, can influence blade wear. Excessive dust and debris can contribute to accelerated wear.
12. Usage Patterns:
How often and for how long the blade is used will also affect its lifespan. Intermittent use with proper cooling periods can extend life compared to continuous use which may overheat the blade.
By managing these factors effectively, operators can maximize the life of their block cutter blades, ensuring efficient and cost-effective stone cutting operations.
Comparing Block Cutters and Wire Saws for Cutting Large Stone Blocks
When comparing block cutters and wire saws for cutting large stone blocks, it’s important to consider various dimensions, including precision, speed, versatility, operational costs, and the quality of the finished product. Here’s a contrast of the two methods across these dimensions:
Precision:
Block Cutters:
Advantages: They provide uniform cuts with consistent depth and are excellent for straight cuts.
Disadvantages: They may not be as precise for intricate or complex shapes compared to wire saws.
Wire Saws:
Advantages: High precision in cutting complex and irregular shapes due to their flexibility.
Disadvantages: The precision depends on the tensioning and the operator’s skill, which can vary.
Speed:
Block Cutters:
Advantages: Faster at producing straight cuts and typically have shorter setup times for simple cutting tasks.
Disadvantages: Slower when it comes to complex cuts or shapes, as multiple setups may be required.
Wire Saws:
Advantages: Can be faster for complex cuts that would require multiple setups with a block cutter.
Disadvantages: The cutting process can be slower due to the sawing action and the need for constant cooling.
Versatility:
Block Cutters:
Advantages: Ideal for producing standard slab sizes and thicknesses, great for repetitive tasks.
Disadvantages: Less versatile in terms of the variety of shapes and sizes they can produce.
Wire Saws:
Advantages: Extremely versatile, able to cut complex shapes and large blocks that are difficult for block cutters.
Disadvantages: The versatility can come at the cost of increased complexity in setup and operation.
Operational Costs:
Block Cutters:
Advantages: Generally lower operational costs due to simpler mechanics and less wear on the components.
Disadvantages: The blades can be expensive to replace if damaged or worn out.
Wire Saws:
Advantages: Wire replacement can be less costly compared to replacing large blades.
Disadvantages: Higher operational costs due to more complex machinery and the need for frequent wire replacements.
Quality of Finished Product:
Block Cutters:
Advantages: Produces clean and straight edges, ideal for tiles and countertop slabs.
Disadvantages: May cause chipping or flaking on the cut surface if not properly maintained.
Wire Saws:
Advantages: Able to produce smoother cuts with minimal damage to the stone surface.
Disadvantages: The quality of the finish can be affected by the wire’s tension and the operator’s expertise.
When choosing between block cutters and wire saws, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of the job. Block cutters are typically favored for their speed and efficiency in producing standard-sized materials, whereas wire saws are chosen for their flexibility and ability to handle complex cuts. Operational costs, precision needs, and the desired quality of the finished product will all play a role in determining the most suitable equipment for cutting large stone blocks.
The ability to cut large stone blocks efficiently and accurately is essential in many fields. With advancements in technology, the equipment available today can meet the most demanding cutting requirements. From the raw power of wire saws and block cutters to the finesse of CNC machines and water jet cutters, each piece of equipment has its unique advantages that cater to different aspects of stone cutting. By understanding the capabilities of these tools, professionals in the stone industry can select the right equipment for their specific needs, ensuring that their projects are executed with excellence and precision.
